low end tidal co2 treatment
On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing. The gradient is the difference between the arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure PaCO 2 and the etCO 2 partial pressure is a result of the relationship between ventilation and perfusion or rather ventilation-perfusion matching VQ.
Severe runs of VPCs can be treated with.
. This causes a higher concentration of CO2 to be exhaled with each breath and for ETCO2 to rise. Since reduced breathing in the sick those with less than 20 s for the body oxygen test or more than 12 Lmin for minute ventilation at rest is done with increased respiratory frequency and reduced tidal volume they can get low etCO 2 numbers while in reality their alveolar and arterial CO2 will be increasing during the whole session eg 10-15 minutes. However EtCO2 is an extremely powerful surrogate for endotracheal tube ETT P osition CPR Q uality R eturn of spontaneous circulation ROSC S trategies for treatment.
This study investigates the association of initial in-hospital ETCO2 and patient outcomes as well as the utility of ETCO2 as a predictive aid for blood transfusion. Treatment is directed toward the specific cause of the VPCs. The normal end-tidal capnography wave form is basically a rounded rectangle.
The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide measured at the end of exhalation which represents alveolar carbon dioxide concentration. 2 mgkg of lidocaine IV given as a single bolus.
From clinical experience and based on published case reports 13 14 we hypothesized that end-tidal CO 2 etCO 2 a nearly universally available clinical parameter in the operating room OR and with a time constant for changes of dozens of seconds could improve clinical reasoning when AHR is a possible diagnosis in patients under general anaesthesia GA. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition. Early identification of diabetic ketoacidosis DKA may improve clinical outcomes.
Importantly evidence of low end-tidal CO2 can be seen across a variety of anxiety disorders and has been shown to predict treatment-dropout in patients with. Low end tidal co2 during cpr. An etCO2 value below 26 kPa 20 mm Hg could be useful for prompt diagnosis of severe intra.
When a person is breathing in it. Therefore correlation between the end tidal CO2 and an ABGVBG measurement is needed to confirm the diagnosis of hypocapnia. Prior studies suggest exhaled end tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 provides a non-invasive real-time method to screen for DKA in the emergency department ED.
Low end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 is associated with mortality and hemorrhagic shock in trauma but the relationship between low ETCO2 and important clinical variables is not known. This dose can be repeated up to a max of 8 mgkg IV over a course of 5 to 10 minutes. Administer oxygen bronchodilators corticosteroids and CPAP.
In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. End tidal CO2 revealing a substantially low CO2 measurement also suggests hypocapnia eg etCO2. An etCO2 value below 26 kPa 20 mm Hg could be useful for prompt diagnosis of severe intra-anaesthetic AHR and could facilitate early treatment with titrated doses of epinephrine.
2 See Figure 1 p. End Tidal CO2 ETCO2 or PetCO2 - the level of partial pressure of carbon dioxide released at end of expiration. However this may also be caused by pulmonary dysfunction with an increase in dead space volume.
When calculating the gradient the clinician is comparing the carbon dioxide CO 2 sampled from the ABG. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. Capnography the waveform measurement of exhaled end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 is a well-known tool in EMS.
EtCO 2 is a continuous variable determined by basal metabolic rate cardiac output. This a retrospective cohort study among patients who activated Emergency Medical Services EMS. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a measure of metabolism perfusion and ventilation.
The hinges represent the first and third quartiles the notches represent the 95 confidence interval CI of the median and the whiskers extend to 15 interquartile range. 48 When a person is breathing out CO 2 the graph goes up. A waveform tracking the level of carbon.
The results therefore suggest that in mechanically ventilated patients with severe postinduction hypotension ETco2 should be. Recent clinical trial research suggests that baseline low end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 the biological marker of hyperventilation may predict poorer response to cognitive-behavioral therapy CBT for anxiety-related disorders. In the ED we typically think of a EtCO2 as a marker of perfusion and ventilation.
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. The treatment approach for exacerbations of chronic bronchitis and emphysema is the same. Severe runs of VPCs can be treated with.
EtCO 2 is a continuous variable determined by basal metabolic rate cardiac output. Supplemental oxygen administration is vital for hypoxic COPD patients but too much oxygen may worsen CO2 retention and be harmful 2. The height of the capnography waveform accompanies this number on the monitor as well as the.
Assuming that ventilation and perfusion is normal ETCO 2 is approximately equal to the arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. Maximum end-tidal carbon dioxide Et co 2 within 5 minutes of the onset of mechanical ventilation in the operating room ORBox plot with data points overlaid.
More Than Just a Number. From a retrospective single-center case-control study comparing low end-tidal carbon dioxide ETco2 postinduction in hypotensive patients due to anaphylaxis compared to other causes a low ETco2 contributed to the diagnosis of anaphylaxis. A constant rate of infusion of lidocaine between 25 to 80 mcgkgmin may be used.
In the setting of a suspected pneumothorax a high or increasing ETCO2 above 45 mm Hg suggests.

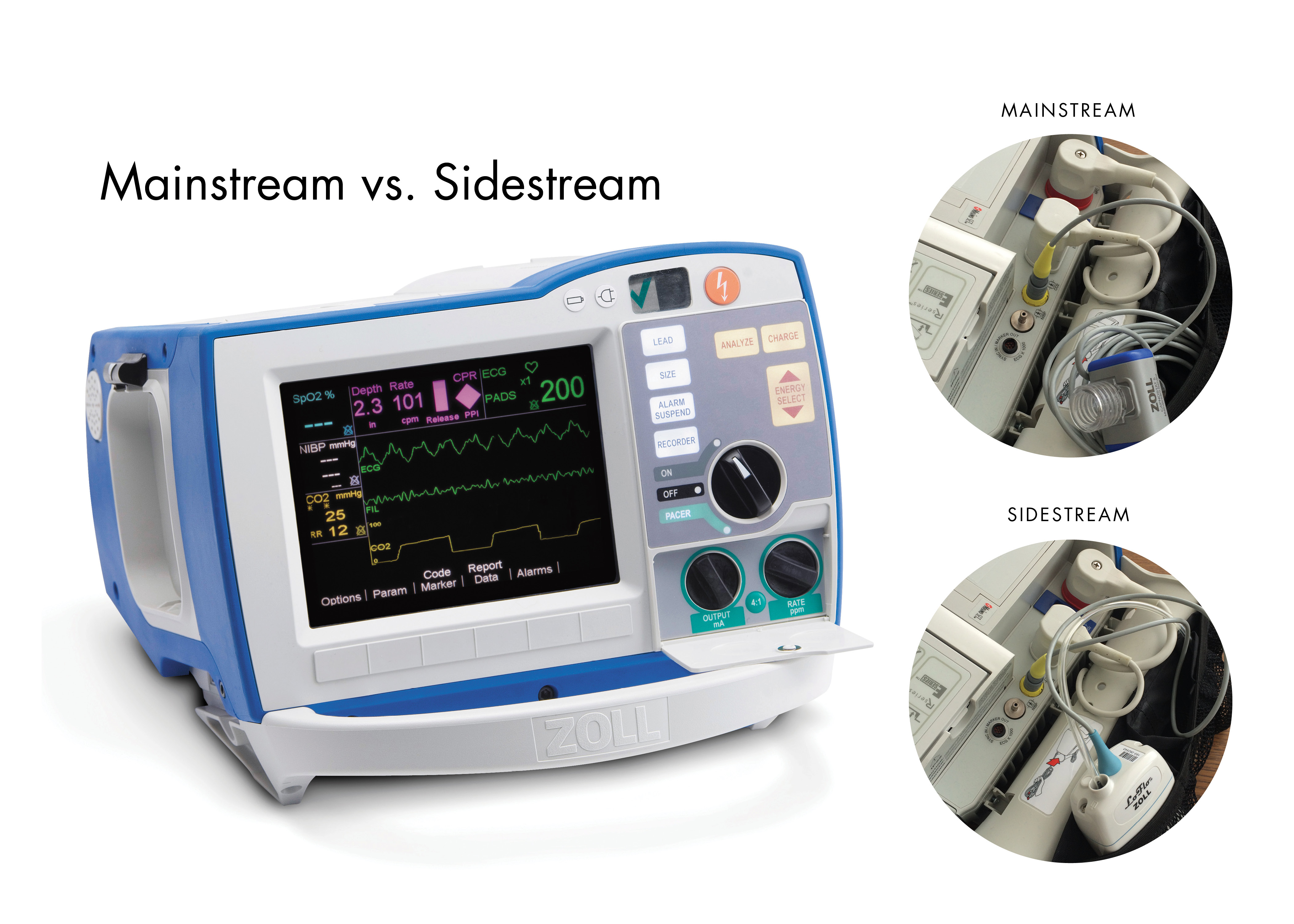
R Series End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Zoll Medical

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

The Critical Role Of Capnography Bound Tree
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog
End Tidal Co2 Etco2 Capnography For R Series Zoll Medical

A Systematic Approach To Capnography Waveforms Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

End Tidal C02 Worth The Investment
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

End Tidal Co2 Respiratory Therapy Medical Knowledge Icu Nursing

Evidence Supports Using End Tidal Carbon Dioxide To Detect Prehospital Sepsis Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

End Tidal Co2 Patient Tidal Respiratory Therapy

Capnograph Note Try To Maintain Etco2 Above 10mmhg During Cpr Paramedic School Emergency Nursing Respiratory Therapy Student
5 Medical Conditions Where Capnography Can Affect Bls Care Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Wave Form Capnography Emergency Medicine Icu Nursing Respiratory Care

Capnography Etco2 And Airway Management Rt
End Tidal Co2 Levels Vs Arterial Co2 Levels In Children With Tbi Healthmanagement Org

